Mouse Brain Tissue Sections
A coronal thin section of mouse brain (presented above) was immunofluorescently labeled for heavy chain neurofilament subunits (present in neurons) with chicken anti-NF-H antibodies followed by goat anti-chicken secondary antibodies conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488.
In addition, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), which is strongly and specifically expressed in various astroglia and neural stem cells, was targeted in the specimen with rabbit anti-GFAP monoclonal antibodies visualized with goat anti-rabbit antibodies conjugated to Alexa Fluor 568.
Nuclear DNA was counterstained with the probe Hoechst 33342.
Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to a Nikon Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks. During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
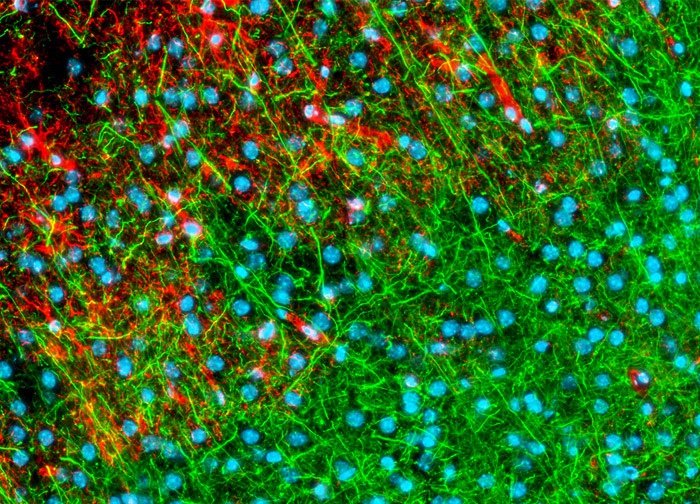
Mouse Brain Tissue Sections
The neuron-specific intermediate filaments known as neurofilaments were targeted in the mouse brain coronal thin section shown above with chicken anti NF-H antibodies followed by goat anti-chicken secondary antibodies conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488. In addition, glial fibrillary acidic protein, an intermediate filament protein that is a key structural element of astroglia, was immunofluorescently labeled with primary anti-GFAP rabbit monoclonal antibodies followed by goat anti-rabbit Fab fragments conjugated to Alexa Fluor 568.
Hoechst 33342 was employed as a nuclear counterstain.
Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to a Nikon Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks. During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Mouse Kidney Tissue
Lectins are carbohydrate-binding proteins that selectively bind to specific configurations of sugar molecules.
Certain oligosaccharide residues are found on cell surfaces and covalently linked to specific cellular components.
Consequently, lectins can be utilized to identify various cell types and cell constituents.
The lectin wheat germ agglutinin (WGA) binds to N-acetylglucosamine and sialic acid residues and is commonly used to identify the Golgi complex in mammalian cells.
The mouse kidney tissue sample presented in the digital image above was labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to WGA.
In addition, the specimen was labeled for F-actin and DNA with Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin and DAPI, respectively.
Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks.
During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Mouse Kidney Tissue
The mouse kidney tissue sample presented in the digital image above was triple labeled before imaging.
Alexa Fluor 568 (red fluorescence emission) conjugated to phalloidin was utilized to target polymerized actin (F-actin) and Alexa Fluor 488 (green emission) conjugated to wheat germ agglutinin was used to target sialic acid and N-acetylglucosaminyl residues.
The popular nuclear and chromosome counterstain DAPI, which emits blue fluorescence upon binding to AT regions of DNA, was also employed. Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks.
During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
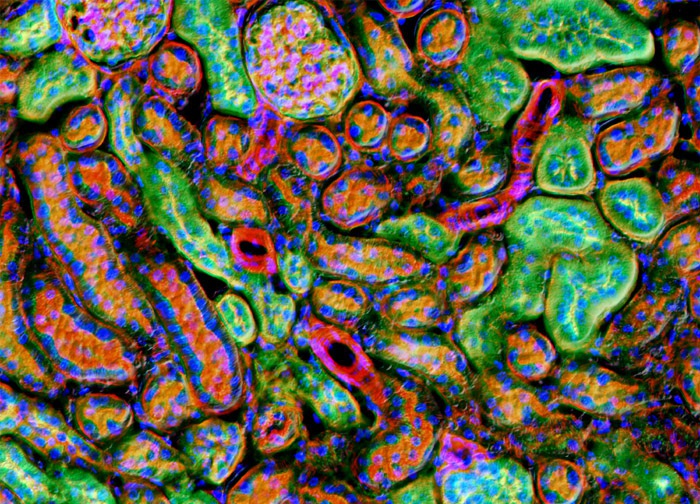
Mouse Kidney Tissue
Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to the lectin wheat germ agglutinin, which selectively binds to N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylneuraminic (sialic acid) residues and is frequently used to localize the Golgi network in mammalian cells, was utilized to label the mouse kidney tissue sample illustrated in the digital image above.
The specimen was labeled for filamentous actin with Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin and for nuclear DNA with DAPI.
Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks.
During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Mouse Kidney Tissue
In order to localize a red fluorescent tag to filamentous actin in the mouse kidney tissue presented in the digital image above, the specimen was labeled with Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin, a phallotoxin often utilized in cell biology.
Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to the lectin wheat germ agglutinin, which selectively binds to N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylneuraminic residues, was also applied to the tissue sample.
Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks.
During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Mouse Kidney Tissue
Phalloidin is a phallotoxin isolated from the highly poisonous Amanita phalloides mushroom that binds polymerized actin (F-actin).
Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin was utilized to target the filamentous actin in the mouse kidney tissue sample presented in the digital image above.
Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated to the lectin wheat germ agglutinin and the nucleic acid stain DAPI were also employed to label the specimen. Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks. During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Mouse Intestine Tissue
Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to the lectin wheat germ agglutinin, which selectively binds to N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylneuraminic (sialic acid) residues and is frequently used to target the Golgi apparatus in mammalian cells, was utilized to label the mouse intestine tissue sample depicted in the digital image above.
The specimen was counterstained for filamentous actin with Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin and for nuclear DNA with SYTOX Green.
Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks.
During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Mouse Intestine Tissue
The sample of mouse intestine tissue presented above was triple labeled before imaging.
Alexa Fluor 568 (red emission) conjugated to phalloidin was utilized to target F-actin and Alexa Fluor 350 (blue emission) conjugated to wheat germ agglutinin was used to target sialic acid and N-acetylglucosaminyl residues.
The popular green fluorescent nuclear and chromosome counterstain SYTOX Green was also employed. Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks.
During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Mouse Intestine Tissue
In order to localize a red fluorescent tag to filamentous actin in the sample of mouse intestine tissue presented in the digital image above, the specimen was labeled with Alexa Fluor 568 conjugated to phalloidin, a phallotoxin commonly utilized in cell biology.
Another Alexa Fluor dye, Alexa Fluor 350, conjugated to the lectin wheat germ agglutinin, which selectively binds to N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylneuraminic residues, was also applied to the tissue sample, as was the nucleic acid stain SYTOX Green. Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks.
During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Mouse Intestine Tissue
Phallotoxins are peptides isolated from the toxic Amanita phalloides mushroom that bind filamentous actin.
A phallotoxin, phalloidin, conjugated to Alexa Fluor 568 was employed to target the F-actin in the mouse intestine tissue sample featured in the digital image above.
Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to the lectin wheat germ agglutinin was also utilized to label the specimen.
Cell nuclei were targeted with the popular nucleic acid stain SYTOX Green. Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks.
During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Sheep Bladder Tissue
The filamentous actin present in a sample of sheep bladder tissue (illustrated above) was targeted with Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to a phallotoxin, phalloidin. In addition, the specimen was stained with Oregon Green 488 conjugated to wheat germ agglutinin, a lectin that selectively binds N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylneuraminic (sialic acid) residues.
SYTOX Orange was employed to stain nucleic acids. Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks.
During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Sheep Lung Tissue
The sample of sheep lung tissue presented in the digital image above was labeled with Alexa Fluor 350 (blue fluorescence) conjugated to wheat germ agglutinin, a lectin that selectively binds N-acetylglucosamine and sialic acid residues.
The specimen was also labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 (green) conjugated to phalloidin and SYTOX Orange, targeting F-actin and nuclear DNA, respectively. Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks.
During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Sheep Tongue Tissue
In order to localize a blue fluorescent tag to F-actin in the sheep tongue tissue sample presented in the digital image above, the specimen was labeled with Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to phalloidin, a commonly used actin-binding phallotoxin.
Oregon Green 488 conjugated to the lectin wheat germ agglutinin, which selectively binds to N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylneuraminic residues, was also applied to the tissue sample.
Cell nuclei were counterstained with SYTOX Orange. Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks.
During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
Sheep Tongue Tissue
Phalloidin is a phallotoxin isolated from the highly toxic Amanita phalloides mushroom that binds polymerized actin (F-actin).
Alexa Fluor 350 conjugated to phalloidin was utilized to target filamentous actin in the sheep tongue tissue sample featured in the digital image above. Oregon Green 488 conjugated to the lectin wheat germ agglutinin and the nucleic acid stain SYTOX Orange were also employed to label the specimen.
Images were recorded in grayscale with a 12-bit digital camera coupled to either a Nikon E-600 or Eclipse 80i microscope equipped with bandpass emission fluorescence filter optical blocks.
During the processing stage, individual image channels were pseudocolored with RGB values corresponding to each of the fluorophore emission spectral profiles.
스펙



